What is JSP. How to create one JSP application in Eclipse
JSP - Java Server Pages Technology
Java
Server Pages (JSP) technology allows you to easily create web content that has
both static and dynamic components. JSP technology makes available all the
dynamic capabilities of Java Servlet technology but provides a more natural
approach to creating static content.
The main features of JSP technology are as follows:
·
A language for developing JSP pages,
which are text-based documents that describe how to process a request and
construct a response
·
An expression language for accessing
server-side objects
·
Mechanisms for defining extensions to
the JSP language
JSP technology also contains an API that is used by
developers of web containers. Using this technology developer can design UI for
client (browser) as well as business logic for communicating server. A JSP file
contains HTML, JavaScript, CSS & Java codes.
JSP technology
is used to create web application just like Servlet technology. It can be
thought of as an extension to Servlet because it provides more functionality
than servlet such as expression language, JSTL, etc.
A JSP page consists of HTML tags and JSP tags. The JSP pages are
easier to maintain than Servlet because we can separate designing and
development. It provides some additional features such as Expression Language,
Custom Tags, etc.
Advantages of JSP over Servlet
There are many advantages of JSP over the Servlet. They are as
follows:
1) Extension to
Servlet
JSP technology is the extension to Servlet technology. We can
use all the features of the Servlet in JSP. In addition to, we can use implicit
objects, predefined tags, expression language and Custom tags in JSP, which
makes JSP development easy.
2)
Easy to maintain
JSP can be easily managed because we can easily separate our
business logic with presentation logic. In Servlet technology, we mix our
business logic with the presentation logic.
3) Fast Development:
No need to recompile and redeploy
If JSP page is modified, we don't need to recompile and redeploy
the project. The Servlet code needs to be updated and recompiled if we have to
change the look and feel of the application.
4) Less code than
Servlet
In JSP, we can use many tags such as action tags, JSTL, custom
tags, etc. that reduces the code. Moreover, we can use EL, implicit objects,
etc.
5)
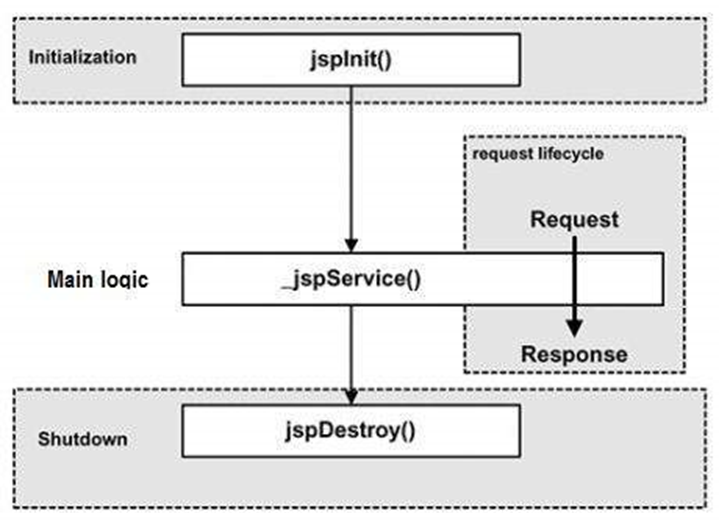
The Lifecycle of a JSP Page
The
JSP pages follow these phases:
- Translation of
JSP Page
- Compilation of
JSP Page
- Class loading
(the classloader loads class file)
- Instantiation
(Object of the Generated Servlet is created).
- Initialization
(the container invokes jspInit()
method).
- Request
processing (the container invokes _jspService()
method).
- Destroy (the
container invokes jspDestroy() method).
Here jspInit(),_jspService(), and jspDestroy are the
3 life cycle methods of JSP.
Unlike
other java files, user no need to compile a JSP files. Once it deployed in web server,
JSP container compiles the JSP files and create equivalent _java files and its
class files.
Every
JSP container having one JSP translator. JSP page is translated into Servlet by
the help of JSP translator. The JSP translator is a part of the web server
which is responsible for translating the JSP page into Servlet. After that,
Servlet page is compiled by the compiler and gets converted into the class
file. Moreover, all the processes that happen in Servlet are performed on JSP
later like initialization, committing response to the browser and destroy.
6)
A Simple JSP Page Example
Localized Date Form
The JSP page, index.jsp,
appears below; it is a typical mixture of static HTML markup and JSP elements.
If you have developed web pages, you are probably familiar with the HTML
document structure statements (<head>, <body>, and so on) and the HTML statements that
create a form (<form>)
and a menu (<select>).
The
lines in bold in the example code contain the following types of JSP
constructs:
·
A page directive (<%@page
... %>) sets the content type returned by the page.
·
Tag library directives (<%@taglib
... %>) import custom tag libraries.
·
jsp:useBean is a standard element that creates an object
containing a collection of locales and initializes an identifier that points to
that object.
·
JSP expression language expressions (${ }) retrieve the value of object properties. The
values are used to set custom tag attribute values and create dynamic content.
·
Custom tags set
a variable (c:set),
iterate over a collection of locale names (c:forEach),
and conditionally insert HTML text into the response (c:if, c:choose, c:when, c:otherwise).
·
jsp:setProperty is another standard element that sets the value
of an object property.
·
A function (f:equals)
tests the equality of an attribute and the current item of a collection. (A
built-in == operator
is usually used to test equality.)
Here is the example of JSP page:
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="/functions" prefix="f" %>
<head>
<title>Localized Dates</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<c:set var="selectedLocaleString" value="${param.locale}" />
<c:set var="selectedFlag" value="${!empty selectedLocaleString}" />
<b>Locale:</b>
<select name=locale>
<c:forEach var="localeString" items="${locales.localeNames}" >
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${selectedFlag}">
<c:choose>
<c:when
test="${f:equals(selectedLocaleString, localeString)}" >
<option selected>${localeString}</option>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<option>${localeString}</option>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<option>${localeString}</option>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</c:forEach>
</select>
<input type="submit" name="Submit" value="Get Date">
</form>
<c:if test="${selectedFlag}" >
<jsp:setProperty name="locales"
property="selectedLocaleString"
value="${selectedLocaleString}" />
<jsp:useBean id="date" class="mypkg.MyDate"/>
<jsp:setProperty name="date" property="locale"
value="${locales.selectedLocale}"/>
<b>Date: </b>${date.date}</c:if>
</body>
</html>
Process To deploy the MyFirstWeb application with Eclipse IDE :-
à Type the project name
as “MyFirstWeb”
à Click on Next à tick on web.xml and
click on Finish.
2) Now open your project (double click on your project name)
à Right click on WebApp
àtype the file name as index.jsp
and click on Finish
à Now your index.jsp file is open à type the souce code in file editor area and save
<head>
<title>My First Web Page</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<tr>
<td>Enter Your First Name :</td>
<td><input type="text" name="txtFirstName" value=""></td>
<tr>
<td>Enter Your Second Name :</td>
<td><input type="text" name="txtSecondName" value=""></td>
</table>
à Using above process
create another jsp file “display.jsp”.
àtype the file name as display.jsp
and click on Finish
à open display.jsp,
write the below code and save it.
String sFirstName = "";
String sSecondName = "";
if(request.getParameter("txtFirstName")!=null){
sFirstName = request.getParameter("txtFirstName");
}
if(request.getParameter("txtSecondName")!=null){
sSecondName = request.getParameter("txtSecondName");
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
<html>
<head>
<title>My Second Web Page</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<tr>
<td>Your First Name :</td>
<td><%=sFirstName%></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Your Second Name :</td>
<td><%=sSecondName%></td>
</tr>
</table>
</html>
4)
Now we have to import external jars for our project
à Right click on your
project à Build
patch à
configure build path
à
à Select the
servlet-api.jar and open
5)
How to run application in Eclipse
à Right click on
project à
Run as à
Run on Server
à select your server à Finish
è Now your application will start and it will show below output
à Next Page showing your result....





















Nice and easy to learn project
ReplyDelete