Collections in Java
Collections in Java
The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate the group of objects.
Java Collections can achieve all the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion.
Java Collection means a single unit of objects. Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet).
What is Collection in Java
A Collection represents a single unit of objects, i.e., a group.
What is a framework in Java
- It provides readymade architecture.
- It represents a set of classes and interfaces.
- It is optional.
What is Collection framework
The Collection framework represents a unified architecture for storing and manipulating a group of objects. It has:
- Interfaces and its implementations, i.e., classes
- Algorithm
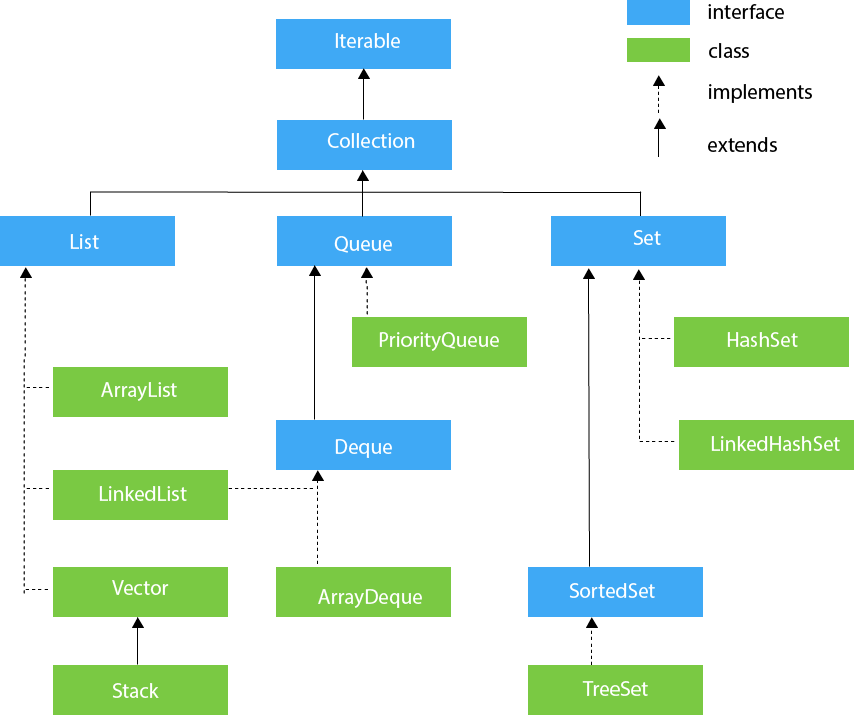
Hierarchy of Collection Framework
Let us see the hierarchy of Collection framework. The java.util package contains all the classes and interfaces for the Collection framework.
Methods of Collection interface
There are many methods declared in the Collection interface as follows:
|
No |
Method |
Description |
|
1 |
public
boolean add(E e) |
It is
used to insert an element in this collection. |
|
2 |
public
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) |
It is
used to insert the specified collection elements in the invoking collection. |
|
3 |
public
boolean remove(Object element) |
It is
used to delete an element from the collection. |
|
4 |
public
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) |
It is
used to delete all the elements of the specified collection from the invoking
collection. |
|
5 |
default
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) |
It is
used to delete all the elements of the collection that satisfy the specified
predicate. |
|
6 |
public
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) |
It is
used to delete all the elements of invoking collection except the specified
collection. |
|
7 |
public
int size() |
It
returns the total number of elements in the collection. |
|
8 |
public
void clear() |
It
removes the total number of elements from the collection. |
|
9 |
public
boolean contains(Object element) |
It is
used to search an element. |
|
10 |
public
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) |
It is
used to search the specified collection in the collection. |
|
11 |
public
Iterator iterator() |
It
returns an iterator. |
|
12 |
public
Object[] toArray() |
It
converts collection into array. |
|
13 |
public
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a) |
It
converts collection into array. Here, the runtime type of the returned array
is that of the specified array. |
|
14 |
public
boolean isEmpty() |
It checks
if collection is empty. |
|
15 |
default
Stream<E> parallelStream() |
It
returns a possibly parallel Stream with the collection as its source. |
|
16 |
default
Stream<E> stream() |
It
returns a sequential Stream with the collection as its source. |
|
17 |
default
Spliterator<E> spliterator() |
It
generates a Spliterator over the specified elements in the collection. |
|
18 |
public
boolean equals(Object element) |
It
matches two collections. |
|
19 |
public
int hashCode() |
It
returns the hash code number of the collection. |
Collection Interface
The Collection interface is the interface which is implemented by all the classes in the collection framework. It declares the methods that every collection will have. In other words, we can say that the Collection interface builds the foundation on which the collection framework depends.
Some of the methods of Collection interface are Boolean add ( Object obj), Boolean addAll ( Collection c), void clear(), etc. which are implemented by all the subclasses of Collection interface.
List Interface
List interface is the child interface of Collection interface. It inhibits a list type data structure in which we can store the ordered collection of objects. It can have duplicate values.
List interface is implemented by the classes ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, and Stack.
To instantiate the List interface, we must use :
There are various methods in List interface that can be used to insert, delete, and access the elements from the list.
The classes that implement the List interface are given below.
ArrayList
The ArrayList class implements the List interface. It uses a dynamic array to store the duplicate element of different data types. The ArrayList class maintains the insertion order and is non-synchronized. The elements stored in the ArrayList class can be randomly accessed. Consider the following example.
Output:
10 11 12 13
LinkedList
LinkedList implements the Collection interface. It uses a doubly linked list internally to store the elements. It can store the duplicate elements. It maintains the insertion order and is not synchronized. In LinkedList, the manipulation is fast because no shifting is required.
Consider the following example.
Output:
Ravi Papu Sagar Prabhat
Vector
Vector uses a dynamic array to store the data elements. It is similar to ArrayList. However, It is synchronized and contains many methods that are not the part of Collection framework.
Consider the following example.
Output:
Ayush Amitabh Ashish Gulu
Stack
The stack is the subclass of Vector. It implements the last-in-first-out data structure, i.e., Stack. The stack contains all of the methods of Vector class and also provides its methods like boolean push(), boolean peek(), boolean push(object o), which defines its properties.
Example
Output:
Garima
Amrit
Ashish
Priyanka
Iterator interface
| Iterator interface provides the facility of iterating the elements in a forward direction only. |
Methods of Iterator interface
There are only three methods in the Iterator interface as following.
|
No. |
Method |
Description |
|
1 |
public boolean hasNext() |
It returns true if the iterator has
more elements otherwise it returns false. |
|
2 |
public Object next() |
It returns the element and moves
the cursor pointer to the next element. |
|
3 |
public void remove() |
It removes the last elements
returned by the iterator. It is less used. |

Comments
Post a Comment