Decision-Making if-else statement in Java
If Statement
In Java, the "if" statement is used to evaluate a condition. The control of the program is diverted depending upon the specific condition. The condition of the If statement gives a Boolean value, either true or false. In Java, there are four types of if-statements given below.
- Simple if statement
- if-else statement
- if-else-if ladder
- Nested if-statement
Let's understand the if-statements one by one.
1). Simple if statement:
It is the most basic statement among all control flow statements in Java. It evaluates a Boolean expression and enables the program to enter a block of code if the expression evaluates to true.
Syntax of if statement is given below.
Consider the following example in which we have used the if statement in the java code.
Student.java
Student.java
Output:
x + y is greater than 20
2). if-else statement
The if-else statement is an extension to the if-statement, which uses another block of code, i.e., else block. The else block is executed if the condition of the if-block is evaluated as false.
Syntax:
Consider the following example.
Student.java
Output:
x + y is greater than 20
3). if-else-if ladder:
The if-else-if statement contains the if-statement followed by multiple else-if statements. In other words, we can say that it is the chain of if-else statements that create a decision tree where the program may enter in the block of code where the condition is true. We can also define an else statement at the end of the chain.
Syntax of if-else-if statement is given below.
Consider the following example.
Student.java
Output:
Delhi
4). Nested if-statement
In nested if-statements, the if statement can contain a if or if-else statement inside another if or else-if statement.
Syntax of Nested if-statement is given below.
Consider the following example.
Student.java
Output:
Delhi
Java If-else Statement
The Java if statement is used to test the condition. It checks boolean condition: true or false. There are various types of if statement in Java.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- if-else-if ladder
- nested if statement
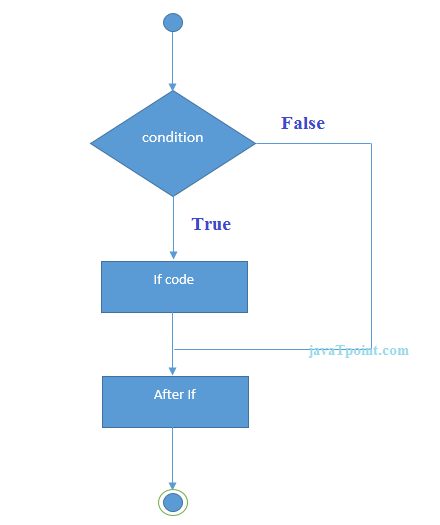
Java if Statement
The Java if statement tests the condition. It executes the if block if condition is true.
Syntax:
Example:
Output:
Age is greater than 18
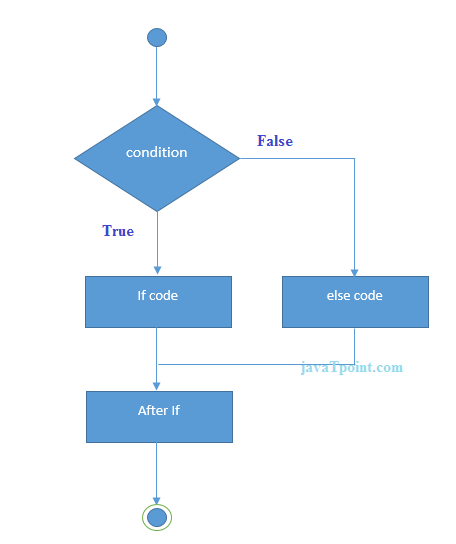
Java if-else Statement
The Java if-else statement also tests the condition. It executes the if block if condition is true otherwise else block is executed.
Syntax:
Example:
Output:
odd number
Leap Year Example:
A year is leap, if it is divisible by 4 and 400. But, not by 100.
Output:
LEAP YEAR
Using Ternary Operator
We can also use ternary operator (? :) to perform the task of if...else statement. It is a shorthand way to check the condition. If the condition is true, the result of ? is returned. But, if the condition is false, the result of : is returned.
Example:
Output:
odd number
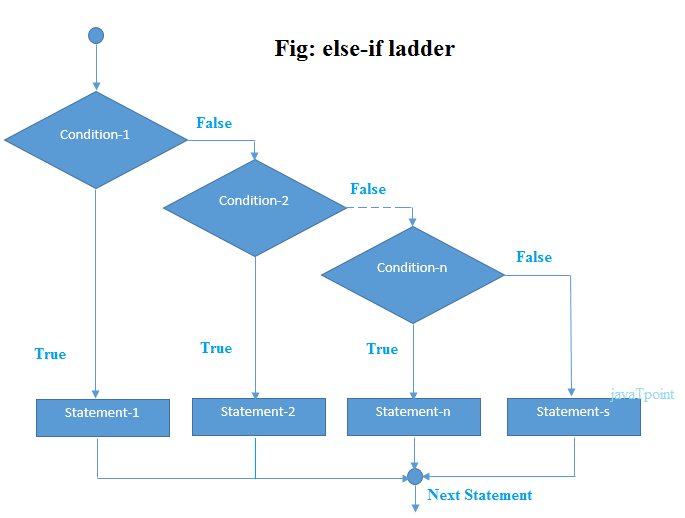
Java if-else-if ladder Statement
The if-else-if ladder statement executes one condition from multiple statements.
Syntax:
Example:
Output:
C grade
Program to check POSITIVE, NEGATIVE or ZERO:
Output:
NEGATIVE
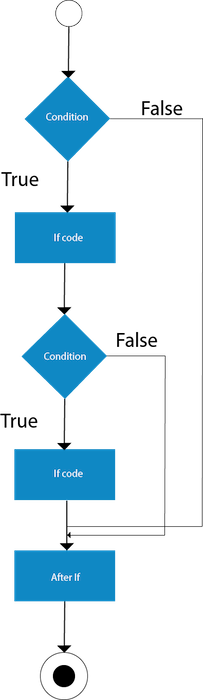
Java Nested if statement
The nested if statement represents the if block within another if block. Here, the inner if block condition executes only when outer if block condition is true.
Syntax:
Example:
Output:
You are eligible to donate blood
Example 2:
Output:
You are not eligible to donate blood

Comments
Post a Comment