Polymorphism in Java
Polymorphism means same name with different behavior and different implementation. Basically it related to multiple method declaration with same name & different behavior or functionality. It may happen in same class or child & parent class both.
In Java, we can achieve polymorphism in two ways :-
1) Method overloading
2) Method overriding.
Method overloading
When we declared same method name with different prototype (different parameters) for achieve multiple task, it is called as method overloading. It may happen in same class or parent and child class.
Example
public String enroll(String DOB){
String sRegNo = "";
//business logic to enroll as a student in db and get sRegNo
System.out.println("Student Registration done based on DOB");
return sRegNo;
}
public String enroll(String DOB, String sPassYear){
String sRegNo = "";
//business logic to enroll as a student in db and get sRegNo
System.out.println("Student Registration done based on DOB & sPassYear");
return sRegNo;
}
}
public class Register{
public static void main(String []args){
String sRegNo = "";
Student st = new Student();
sRegNo = st.enroll("10/10/2002");
sRegNo = st.enroll("10/10/2002", "2020");
}
}
It is also known as Compile time polymorphism or Static binding or early binding. Because during compile time Java Compiler will decide which method need to call in Register class.
Method overriding
When we declared same method name with same prototype (same parameters) for achieve multiple task in child class which is already declared in parent class, it is called as method overriding. It is possible in child class only. Here child class method will overwrite/override the functionality defined in parent class for same method.
Example
public String enroll(String DOB){
String sRegNo = "";
//business logic to enroll as a student in db and get sRegNo
System.out.println("Student Registration done based on DOB");
return sRegNo;
}
}
public class Student extends Batch2020{
public String enroll(String DOB){
String sRegNo = "";
int iAge=0;
//business logic to calculate age and store in iAge variable
if(iAge>25){
//business logic to enroll as a student in db and get sRegNo
System.out.println("Student Registration done based on DOB");
}else{
sRegNo = null;
}
return sRegNo;
}
}
public class Register{
public static void main(String []args){
String sRegNo = "";
Student st = new Student();
sRegNo = st.enroll("10/10/2002");
sRegNo = st.enroll("10/10/1950");
}
}
It is also known as Run time polymorphism or Dynamic binding or Late binding. Because during run time only JVM will decide which method need to call either Student or Batch2020 class in Register.
1) Advantage of method overloading
Method overloading increases the readability of the program.
Different ways to overload the method
There are two ways to overload the method in java
- By changing number of arguments
- By changing the data type
In Java, Method Overloading is not possible by changing the return type of the method only.
1.1) Method Overloading: changing no. of arguments
In this example, we have created two methods, first add() method performs addition of two numbers and second add method performs addition of three numbers.
In this example, we are creating static methods so that we don't need to create instance for calling methods.
Output:
22 33
1.2) Method Overloading: changing data type of arguments
In this example, we have created two methods that differs in data type. The first add method receives two integer arguments and second add method receives two double arguments.
Output:
22 24.9
2) Usage of Java Method Overriding
- Method overriding is used to provide the specific implementation of a method which is already provided by its superclass.
- Method overriding is used for runtime polymorphism
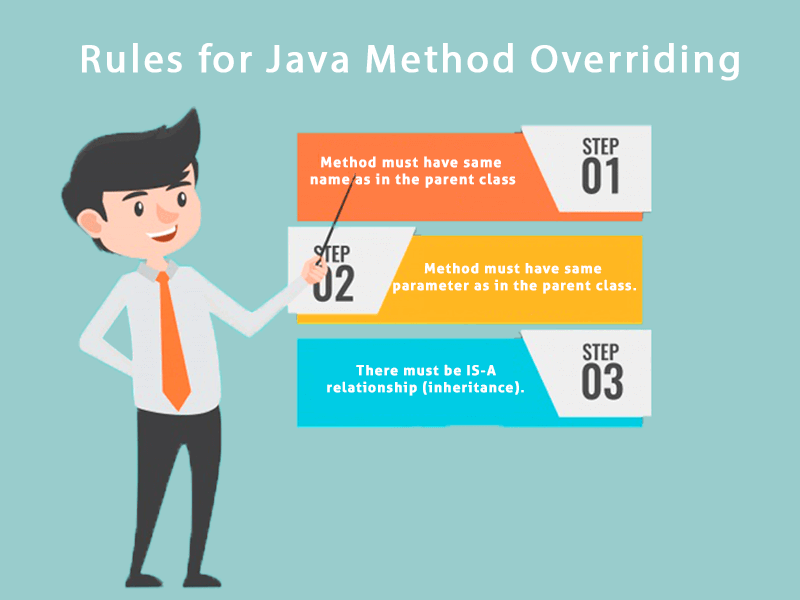
Rules for Java Method Overriding
- The method must have the same name as in the parent class
- The method must have the same parameter as in the parent class.
- There must be an IS-A relationship (inheritance).
Understanding the problem without method overriding
Let's understand the problem that we may face in the program if we don't use method overriding.
Output:
Vehicle is running
Problem is that I have to provide a specific implementation of run() method in subclass that is why we use method overriding.
Example of method overriding
In this example, we have defined the run method in the subclass as defined in the parent class but it has some specific implementation. The name and parameter of the method are the same, and there is IS-A relationship between the classes, so there is method overriding.
Output:
Bike is running safely
A real example of Java Method Overriding
Consider a scenario where Bank is a class that provides functionality to get the rate of interest. However, the rate of interest varies according to banks. For example, SBI, ICICI and AXIS banks could provide 8%, 7%, and 9% rate of interest.
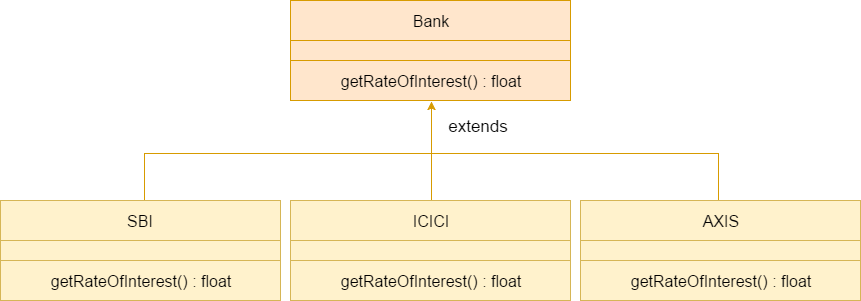
Java method overriding is mostly used in Runtime Polymorphism which we will learn in next pages.
Output :
SBI Rate of Interest: 8 ICICI Rate of Interest: 7 AXIS Rate of Interest: 9
Can we override static method?
No, a static method cannot be overridden. It can be proved by runtime polymorphism, so we will learn it later.
Why can we not override static method?
It is because the static method is bound with class whereas instance method is bound with an object. Static belongs to the class area, and an instance belongs to the heap area.
Can we override java main method?
No, because the main is a static method.
Difference between method overloading and method overriding in java
There are many differences between method overloading and method overriding in java. A list of differences between method overloading and method overriding are given below:
| No. | Method Overloading | Method Overriding |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | Method overloading is used to increase the readability of the program. | Method overriding is used to provide the specific implementation of the method that is already provided by its super class. |
| 2) | Method overloading is performed within class. | Method overriding occurs in two classes that have IS-A (inheritance) relationship. |
| 3) | In case of method overloading, parameter must be different. | In case of method overriding, parameter must be same. |
| 4) | Method overloading is the example of compile time polymorphism. | Method overriding is the example of run time polymorphism. |
| 5) | In java, method overloading can't be performed by changing return type of the method only. Return type can be same or different in method overloading. But you must have to change the parameter. | Return type must be same or covariant in method overriding. |

Comments
Post a Comment